Spring is a lightweight inversion of control and aspect-oriented container framework.
Spring Architecture ?
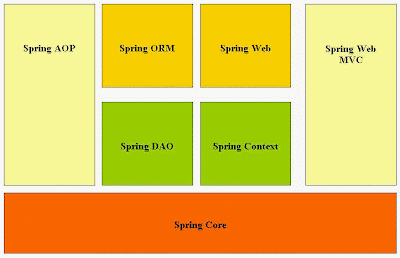
Spring is well-organized architecture consisting of seven modules. Modules in the Spring framework are:
- Spring AOP:One of the key components of Spring is the AOP framework. AOP is used in Spring: To provide declarative enterprise services, especially as a replacement for EJB declarative services. The most important such service is declarative transaction management, which builds on Spring's transaction abstraction. To allow users to implement custom aspects, complementing their use of OOP with AOP
- Spring ORM:The ORM package is related to the database access. It provides integration layers for popular object-relational mapping APIs, including JDO, Hibernate and iBatis.
- Spring Web:The Spring Web module is part of Spring’s web appication development stack, which includes Spring MVC.
- Spring DAO:The DAO (Data Access Object) support in Spring is primarily for standardizing the data access work using the technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO.
- Spring Context:This package builds on the beans package to add support for message sources and for the Observer design pattern, and the ability for application objects to obtain resources using a consistent API.
- Spring Web: MVCThis is the Module which provides the MVC implementations for the web applications.
- Spring Core:The Core package is the most import component of the Spring Framework. This component provides the Dependency Injection features. The BeanFactory provides a factory pattern which separates the dependencies like initialization, creation and access of the objects from your actual program logic.
The following diagram represents the Spring Framework Architecture
Explain SpringMVC Work Flow?
- Client request that goes through when it is handle by a Dispacher Servlet.The Dispacher Servlet is an important part of the web MVC FRAMWORK,which is used for processing the request to the controller and provides the other functionalites for the web application development.
- After initialization of Dispacher Servlet,the spring framwork looks for a file(servlet-name) in the WEB-INF directory of application.
- It also crates the beans,this baens can be used to process request and provide the appropriate views and to be configured in the webapplication context.
- Then next it use HandlerMapping to crate the handler and it is responsible to map the incoming request to the handler.
- We searched for an appropriate handler,such as preprocesser,postprocesser,controller,will be executed in order to prepared a model.
- The controller interface is capable for hndling the request and it returns an appropriate model and vieq.
- The view resolver is used to map b/w view names and actul views.
- Where as view is used for preparation of request and handling over the request to one of the view technologies like JSP,Velocity etc.
Explain Spring?
Lightweight – spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 1MB. And the processing overhead is also very negligible.
Inversion of control (IoC) – Loose coupling is achieved in spring using the technique Inversion of Control. The objects give their dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects. Aspect oriented (AOP) – Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and enables cohesive development by separating application business logic from system services.
Container – Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects.
Framework - Spring provides most of the intra functionality leaving rest of the coding to the developer.
What are the different modules in Spring framework?
The Core container module
Application context module
AOP module (Aspect Oriented Programming)
JDBC abstraction and DAO module
O/R mapping integration module (Object/Relational)
Web module
MVCframework module
What is the Core container module?
This module is provides the fundamental functionality of the spring framework. In this module BeanFactory is the heart of any spring-based application. The entire framework was built on the top of this module. This module makes the spring container.
What is Application context module?
The Application context module makes spring a framework. This module extends the concept of BeanFactory, providing support for internationalization (I18N) messages, application lifecycle events, and validation. This module also supplies many enterprise services such JNDI access, EJB integration, remoting, and scheduling. It also provides support to other framework.
What is AOP module?
The AOP module is used for developing aspects for our Spring-enabled application. Much of the support has been provided by the AOP Alliance in order to ensure the interoperability between Spring and other AOP frameworks. This module also introduces metadata programming to Spring. Using Spring’s metadata support, we will be able to add annotations to our source code that instruct Spring on where and how to apply aspects.
Lightweight – spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 1MB. And the processing overhead is also very negligible.
Inversion of control (IoC) – Loose coupling is achieved in spring using the technique Inversion of Control. The objects give their dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects. Aspect oriented (AOP) – Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and enables cohesive development by separating application business logic from system services.
Container – Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects.
Framework - Spring provides most of the intra functionality leaving rest of the coding to the developer.
What are the different modules in Spring framework?
The Core container module
Application context module
AOP module (Aspect Oriented Programming)
JDBC abstraction and DAO module
O/R mapping integration module (Object/Relational)
Web module
MVCframework module
What is the Core container module?
This module is provides the fundamental functionality of the spring framework. In this module BeanFactory is the heart of any spring-based application. The entire framework was built on the top of this module. This module makes the spring container.
What is Application context module?
The Application context module makes spring a framework. This module extends the concept of BeanFactory, providing support for internationalization (I18N) messages, application lifecycle events, and validation. This module also supplies many enterprise services such JNDI access, EJB integration, remoting, and scheduling. It also provides support to other framework.
What is AOP module?
The AOP module is used for developing aspects for our Spring-enabled application. Much of the support has been provided by the AOP Alliance in order to ensure the interoperability between Spring and other AOP frameworks. This module also introduces metadata programming to Spring. Using Spring’s metadata support, we will be able to add annotations to our source code that instruct Spring on where and how to apply aspects.
What is JDBC abstraction and DAO module?
Using this module we can keep up the database code clean and simple, and prevent problems that result from a failure to close database resources. A new layer of meaningful exceptions on top of the error messages given by several database servers is bought in this module. In addition, this module uses Spring’s AOP module to provide transaction management services for objects in a Spring application.
What are object/relational mapping integration module?
Spring also supports for using of an object/relational mapping (ORM) tool over straight JDBC by providing the ORM module. Spring provide support to tie into several popular ORM frameworks, including Hibernate, JDO, and iBATIS SQL Maps. Spring’s transaction management supports each of these ORM frameworks as well as JDBC.
What is web module?
This module is built on the application context module, providing a context that is appropriate for web-based applications. This module also contains support for several web-oriented tasks such as transparently handling multipart requests for file uploads and programmatic binding of request parameters to your business objects. It also contains integration support with Jakarta Struts.
What is web module?
Spring comes with a full-featured MVC framework for building web applications. Although Spring can easily be integrated with other MVC frameworks, such as Struts, Spring’s MVC framework uses IoC to provide for a clean separation of controller logic from business objects. It also allows you to declaratively bind request parameters to your business objects. It also can take advantage of any of Spring’s other services, such as I18N messaging and validation.
What is a BeanFactory?
A BeanFactory is an implementation of the factory pattern that applies Inversion of Control to separate the application’s configuration and dependencies from the actual application code.
What is AOP Alliance?
AOP Alliance is an open-source project whose goal is to promote adoption of AOP and interoperability among different AOP implementations by defining a common set of interfaces and components.
What is Spring configuration file?
Spring configuration file is an XML file. This file contains the classes information and describes how these classes are configured and introduced to each other.
What does a simple spring application contain?
These applications are like any Java application. They are made up of several classes, each performing a specific purpose within the application. But these classes are configured and introduced to each other through an XML file. This XML file describes how to configure the classes, known as the Spring configuration file.
What are important ApplicationContext implementations in spring framework?
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext – This context loads a context definition from an XML file located in the class path, treating context definition files as class path resources.
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext – This context loads a context definition from an XML file in the filesystem.
XmlWebApplicationContext – This context loads the context definitions from an XML file contained within a web application.
Explain Bean lifecycle in Spring framework?
The spring container finds the bean’s definition from the XML file and instantiates the bean.
Using the dependency injection, spring populates all of the properties as specified in the bean definition.
If the bean implements the BeanNameAware interface, the factory calls setBeanName() passing the bean’s ID.
If the bean implements the BeanFactoryAware interface, the factory calls setBeanFactory(), passing an instance of itself.
If there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their post- ProcessBeforeInitialization() methods will be called.
If an init-method is specified for the bean, it will be called.
Finally, if there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their postProcessAfterInitialization() methods will be called.
What is bean wiring?
Combining together beans within the Spring container is known as bean wiring or wiring. When wiring beans, you should tell the container what beans are needed and how the container should use dependency injection to tie them together.
What are the important beans lifecycle methods?
There are two important bean lifecycle methods. The first one is setup which is called when the bean is loaded in to the container. The second method is the teardown method which is called when the bean is unloaded from the container.
How can you override beans default lifecycle methods?
The bean tag has two more important attributes with which you can define your own custom initialization and destroy methods. Here I have shown a small demonstration. Two new methods fooSetup and fooTeardown are to be added to your Foo class.
What are Inner Beans?
When wiring beans, if a bean element is embedded to a property tag directly, then that bean is said to the Inner Bean. The drawback of this bean is that it cannot be reused anywhere else.
What are the different types of bean injections?
There are two types of bean injections.
1. By setter
2. By constructor
What is Auto wiring?
You can wire the beans as you wish. But spring framework also does this work for you. It can auto wire the related beans together. All you have to do is just set the autowire attribute of bean tag to an autowire type.
What are different types of Autowire types?
There are four different types by which autowiring can be done.
byName
byType
constructor
autodetect
What are the different types of events related to Listeners?
There are a lot of events related to ApplicationContext of spring framework. All the events are subclasses of org.springframework.context.Application-Event. They are
ContextClosedEvent – This is fired when the context is closed.
ContextRefreshedEvent – This is fired when the context is initialized or refreshed. RequestHandledEvent – This is fired when the web context handles any request.
What is an Aspect?
An aspect is the cross-cutting functionality that you are implementing. It is the aspect of your application you are modularizing. An example of an aspect is logging. Logging is something that is required throughout an application. However, because applications tend to be broken down into layers based on functionality, reusing a logging module through inheritance does not make sense. However, you can create a logging aspect and apply it throughout your application using AOP.
What is a Jointpoint?
A joinpoint is a point in the execution of the application where an aspect can be plugged in. This point could be a method being called, an exception being thrown, or even a field being modified. These are the points where your aspect’s code can be inserted into the normal flow of your application to add new behavior.
What is an Advice?
Advice is the implementation of an aspect. It is something like telling your application of a new behavior. Generally, and advice is inserted into an application at joinpoints.
What is a Pointcut?
A pointcut is something that defines at what joinpoints an advice should be applied. Advices can be applied at any joinpoint that is supported by the AOP framework. These Pointcuts allow you to specify where the advice can be applied.
What is an Introduction in AOP?
An introduction allows the user to add new methods or attributes to an existing class. This can then be introduced to an existing class without having to change the structure of the class, but give them the new behavior and state.
What is a Target?
A target is the class that is being advised. The class can be a third party class or your own class to which you want to add your own custom behavior. By using the concepts of AOP, the target class is free to center on its major concern, unaware to any advice that is being applied.
What is a Proxy?
A proxy is an object that is created after applying advice to a target object. When you think of client objects the target object and the proxy object are the same.
What is meant by Weaving?
The process of applying aspects to a target object to create a new proxy object is called as Weaving. The aspects are woven into the target object at the specified joinpoints.
What are the different points where weaving can be applied?
Compile Time
Classload Time
Runtime
What are the different advice types in spring?
Around : Intercepts the calls to the target method
Before : This is called before the target method is invoked
After : This is called after the target method is returned
Throws : This is called when the target method throws and exception
Around : org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor
Before : org.springframework.aop.BeforeAdvice
After : org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice
Throws : org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice
What are the different types of AutoProxying?
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
Metadata autoproxying
What is the Exception class related to all the exceptions that are thrown in spring applications?
DataAccessException - org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException
What kind of exceptions those spring DAO classes throw?
The spring’s DAO class does not throw any technology related exceptions such as SQLException. They throw exceptions which are subclasses of DataAccessException.
What is DataAccessException?
DataAccessException is a RuntimeException. This is an Unchecked Exception. The user is not forced to handle these kinds of exceptions.
How can you configure a bean to get DataSource from JNDI?
java:comp/env/jdbc/myDatasource
Using this module we can keep up the database code clean and simple, and prevent problems that result from a failure to close database resources. A new layer of meaningful exceptions on top of the error messages given by several database servers is bought in this module. In addition, this module uses Spring’s AOP module to provide transaction management services for objects in a Spring application.
What are object/relational mapping integration module?
Spring also supports for using of an object/relational mapping (ORM) tool over straight JDBC by providing the ORM module. Spring provide support to tie into several popular ORM frameworks, including Hibernate, JDO, and iBATIS SQL Maps. Spring’s transaction management supports each of these ORM frameworks as well as JDBC.
What is web module?
This module is built on the application context module, providing a context that is appropriate for web-based applications. This module also contains support for several web-oriented tasks such as transparently handling multipart requests for file uploads and programmatic binding of request parameters to your business objects. It also contains integration support with Jakarta Struts.
What is web module?
Spring comes with a full-featured MVC framework for building web applications. Although Spring can easily be integrated with other MVC frameworks, such as Struts, Spring’s MVC framework uses IoC to provide for a clean separation of controller logic from business objects. It also allows you to declaratively bind request parameters to your business objects. It also can take advantage of any of Spring’s other services, such as I18N messaging and validation.
What is a BeanFactory?
A BeanFactory is an implementation of the factory pattern that applies Inversion of Control to separate the application’s configuration and dependencies from the actual application code.
What is AOP Alliance?
AOP Alliance is an open-source project whose goal is to promote adoption of AOP and interoperability among different AOP implementations by defining a common set of interfaces and components.
What is Spring configuration file?
Spring configuration file is an XML file. This file contains the classes information and describes how these classes are configured and introduced to each other.
What does a simple spring application contain?
These applications are like any Java application. They are made up of several classes, each performing a specific purpose within the application. But these classes are configured and introduced to each other through an XML file. This XML file describes how to configure the classes, known as the Spring configuration file.
What are important ApplicationContext implementations in spring framework?
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext – This context loads a context definition from an XML file located in the class path, treating context definition files as class path resources.
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext – This context loads a context definition from an XML file in the filesystem.
XmlWebApplicationContext – This context loads the context definitions from an XML file contained within a web application.
Explain Bean lifecycle in Spring framework?
The spring container finds the bean’s definition from the XML file and instantiates the bean.
Using the dependency injection, spring populates all of the properties as specified in the bean definition.
If the bean implements the BeanNameAware interface, the factory calls setBeanName() passing the bean’s ID.
If the bean implements the BeanFactoryAware interface, the factory calls setBeanFactory(), passing an instance of itself.
If there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their post- ProcessBeforeInitialization() methods will be called.
If an init-method is specified for the bean, it will be called.
Finally, if there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their postProcessAfterInitialization() methods will be called.
What is bean wiring?
Combining together beans within the Spring container is known as bean wiring or wiring. When wiring beans, you should tell the container what beans are needed and how the container should use dependency injection to tie them together.
What are the important beans lifecycle methods?
There are two important bean lifecycle methods. The first one is setup which is called when the bean is loaded in to the container. The second method is the teardown method which is called when the bean is unloaded from the container.
How can you override beans default lifecycle methods?
The bean tag has two more important attributes with which you can define your own custom initialization and destroy methods. Here I have shown a small demonstration. Two new methods fooSetup and fooTeardown are to be added to your Foo class.
What are Inner Beans?
When wiring beans, if a bean element is embedded to a property tag directly, then that bean is said to the Inner Bean. The drawback of this bean is that it cannot be reused anywhere else.
What are the different types of bean injections?
There are two types of bean injections.
1. By setter
2. By constructor
What is Auto wiring?
You can wire the beans as you wish. But spring framework also does this work for you. It can auto wire the related beans together. All you have to do is just set the autowire attribute of bean tag to an autowire type.
What are different types of Autowire types?
There are four different types by which autowiring can be done.
byName
byType
constructor
autodetect
What are the different types of events related to Listeners?
There are a lot of events related to ApplicationContext of spring framework. All the events are subclasses of org.springframework.context.Application-Event. They are
ContextClosedEvent – This is fired when the context is closed.
ContextRefreshedEvent – This is fired when the context is initialized or refreshed. RequestHandledEvent – This is fired when the web context handles any request.
What is an Aspect?
An aspect is the cross-cutting functionality that you are implementing. It is the aspect of your application you are modularizing. An example of an aspect is logging. Logging is something that is required throughout an application. However, because applications tend to be broken down into layers based on functionality, reusing a logging module through inheritance does not make sense. However, you can create a logging aspect and apply it throughout your application using AOP.
What is a Jointpoint?
A joinpoint is a point in the execution of the application where an aspect can be plugged in. This point could be a method being called, an exception being thrown, or even a field being modified. These are the points where your aspect’s code can be inserted into the normal flow of your application to add new behavior.
What is an Advice?
Advice is the implementation of an aspect. It is something like telling your application of a new behavior. Generally, and advice is inserted into an application at joinpoints.
What is a Pointcut?
A pointcut is something that defines at what joinpoints an advice should be applied. Advices can be applied at any joinpoint that is supported by the AOP framework. These Pointcuts allow you to specify where the advice can be applied.
What is an Introduction in AOP?
An introduction allows the user to add new methods or attributes to an existing class. This can then be introduced to an existing class without having to change the structure of the class, but give them the new behavior and state.
What is a Target?
A target is the class that is being advised. The class can be a third party class or your own class to which you want to add your own custom behavior. By using the concepts of AOP, the target class is free to center on its major concern, unaware to any advice that is being applied.
What is a Proxy?
A proxy is an object that is created after applying advice to a target object. When you think of client objects the target object and the proxy object are the same.
What is meant by Weaving?
The process of applying aspects to a target object to create a new proxy object is called as Weaving. The aspects are woven into the target object at the specified joinpoints.
What are the different points where weaving can be applied?
Compile Time
Classload Time
Runtime
What are the different advice types in spring?
Around : Intercepts the calls to the target method
Before : This is called before the target method is invoked
After : This is called after the target method is returned
Throws : This is called when the target method throws and exception
Around : org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor
Before : org.springframework.aop.BeforeAdvice
After : org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice
Throws : org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice
What are the different types of AutoProxying?
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
Metadata autoproxying
What is the Exception class related to all the exceptions that are thrown in spring applications?
DataAccessException - org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException
What kind of exceptions those spring DAO classes throw?
The spring’s DAO class does not throw any technology related exceptions such as SQLException. They throw exceptions which are subclasses of DataAccessException.
What is DataAccessException?
DataAccessException is a RuntimeException. This is an Unchecked Exception. The user is not forced to handle these kinds of exceptions.
How can you configure a bean to get DataSource from JNDI?
No comments:
Post a Comment